JSON is a lightweight format for storing and transporting data. Because JSON is easy to read and write it’s used by many programming languages not just JavaScript. In this tutorial I’ll show you how to read and write JSON files using Node.js.
Let’s start by first writing data to a JSON file.
Create new JavasScript file named index.js and include the File System (fs) module:
const fs = require("fs");Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Next we’ll declare a books variable that contains our JSON data:
const books = [
{
title: "The Great Gatsby",
author: "F. Scott Fitzgerald",
},
{
title: "Frankenstein",
author: "Mary Shelley",
},
{
title: "The Call of the Wild",
author: "Jack London",
},
];Code language: JavaScript (javascript)We then need to convert the JSON object to a string:
const data = JSON.stringify(books);Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Without converting to a string the data would be written as [object, object].
Now we can write the data to a file using fs.writeFile:
fs.writeFile("./data.json", data, "utf8", (error) => {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
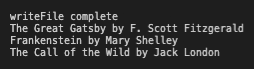
console.log("writeFile complete");
}
});Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Run the code using node index.js and a new data.json file with the JSON data should have been created alongside the index.js file. If no file was created check the error messages that have been logged in the console to debug the problem.
Ok, now that we know how to write JSON data to a file let’s now read that data.
To read data we’ll use fs.readFile in the index.js file as follows:
fs.readFile("./data.json", "utf8", (error, json) => {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
return;
}
try {
const books = JSON.parse(json);
books.forEach((book) => {
console.log(`${book.title} by ${book.author}`);
});
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
});Code language: JavaScript (javascript)This loops through each of the books in our JSON file and logs that data to the console:
That’s all for this tutorial. You should now have an understanding of how to use a simple JSON file to read and store data. While you’re here you may be interested in reading some of our other Node.js tutorials.